As the global economic landscape evolves with simultaneous opportunities and challenges, Chinese companies are actively expanding overseas to explore new global opportunities. On June 6, the China Global Investment Summit 2024 grandly opened in Shenzhen. Mr. Zhu Jianping, Secretary of the Board of INHE Group, was invited to attend the summit and deliver a speech. Drawing on real-life cases from his company, he provided an in-depth analysis of the opportunities and challenges in the overseas market for smart meters and shared INHE's practical experiences and strategies under the Belt and Road Initiative.

What are the Opportunities for Smart Meters?
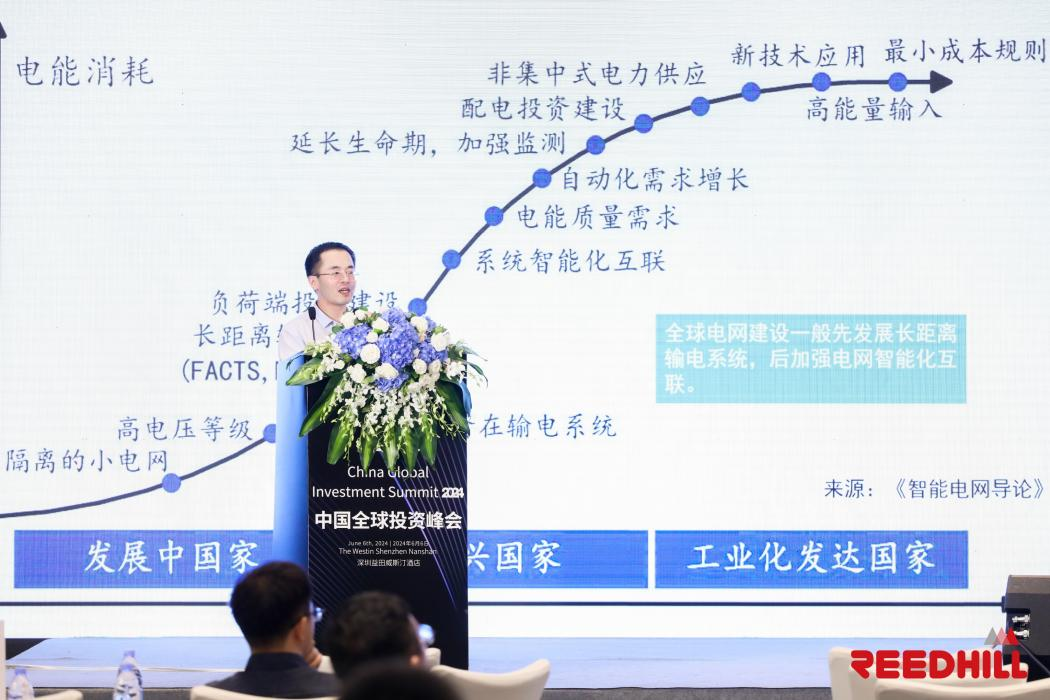
In the post-pandemic era, while many industries have struggled, the power industry has thrived, maintaining high prosperity. Electricity is fundamental to a nation, life, economic production, and industrial development. Regions along the Belt and Road, including Asia, Africa, Europe, and Latin America, have a substantial demand for upgrading their power infrastructure. Mr. Zhu Jianping illustrated this point with a chart showing the different stages of power development across various countries, which encompass developing countries, emerging countries, and industrialized countries.
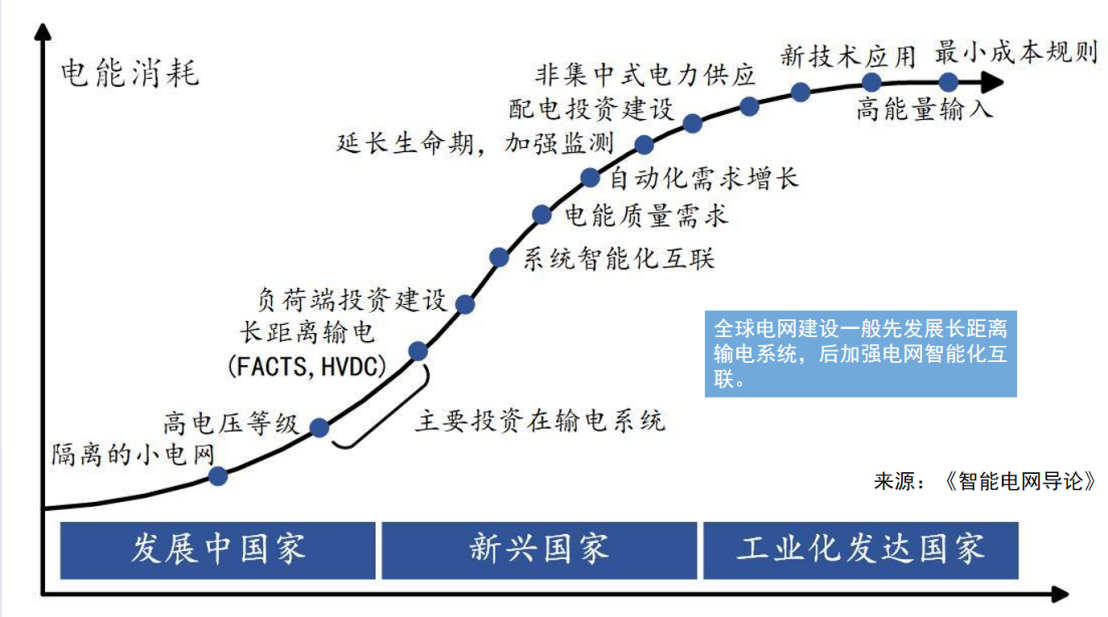
"The bottom curve represents isolated microgrids, commonly found in underdeveloped regions such as Nigeria and Southeast Asia. Specialized Chinese companies have already initiated off-grid power projects in these areas, achieving significant economic benefits. Next is high-voltage, long-distance transmission, which refers to the high-voltage direct current transmission projects previously promoted by China. Above that is the first generation of convenient power infrastructure development, stages that we have already experienced. We are now in the phase of power quality demand and intelligent system interconnection, marked by the new wave of smart meter replacements that began in 2020 and will continue for the next decade."
The future trend is towards decentralized power supply, which is very popular in Europe and the United States. They advocate for distributed energy sources such as home energy storage and photovoltaics. Germany, Italy, North America, the UK and other regions have seen significant demand growth after the pandemic. At the pinnacle is the new technology application stage, which emphasizes high energy input and low cost, such as the substantial power needs of AI computing. This chart is crucial as it demonstrates that our current market aligns with the characteristics of the power development "S-curve" stage.
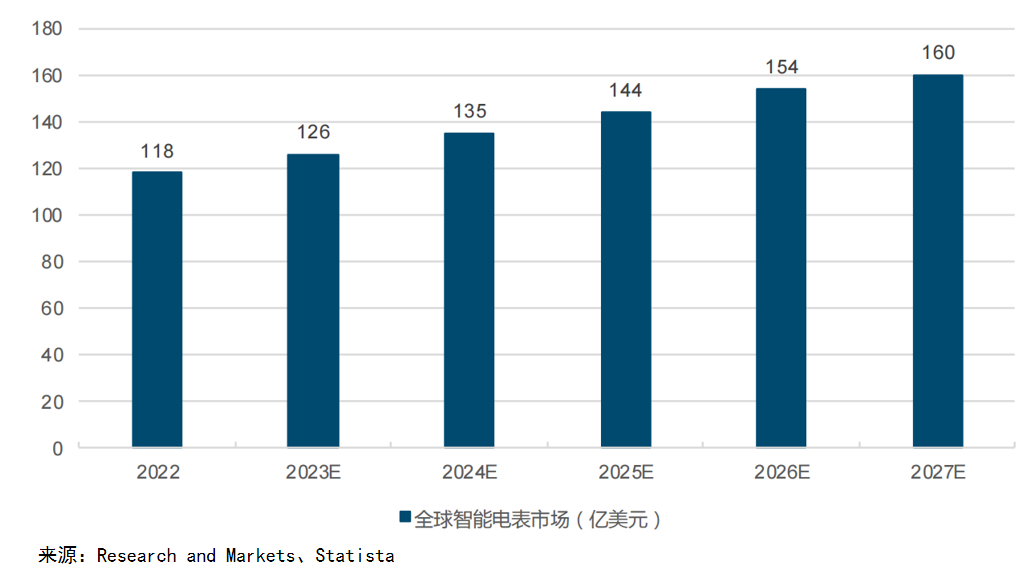
Secondly, considering the smart meter market size, it is estimated to be around 13.5 billion USD in 2024, equivalent to a market size of 100 billion RMB. For a company like Huawei, with a revenue of 700 billion RMB, this market might seem insignificant; however, for smaller companies, the high industry-entry barriers make it difficult to penetrate. Therefore, the smart meter market size is moderate, making it highly suitable and profitable. Unlike some industries, the smart meter market shows steady growth and is not prone to the dramatic spikes and drops seen in the mask market during the pandemic, favoring long-term business operations.
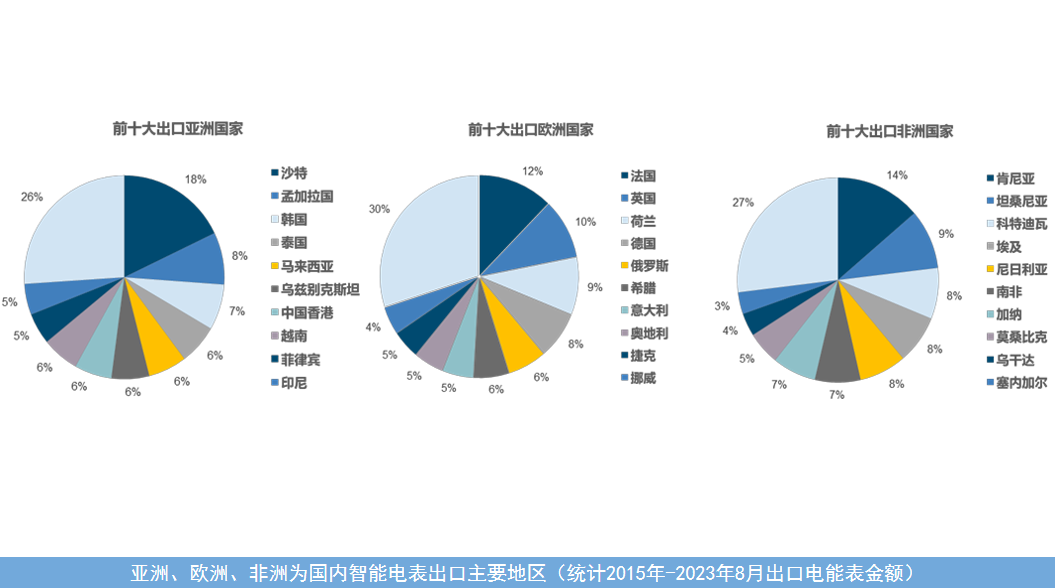
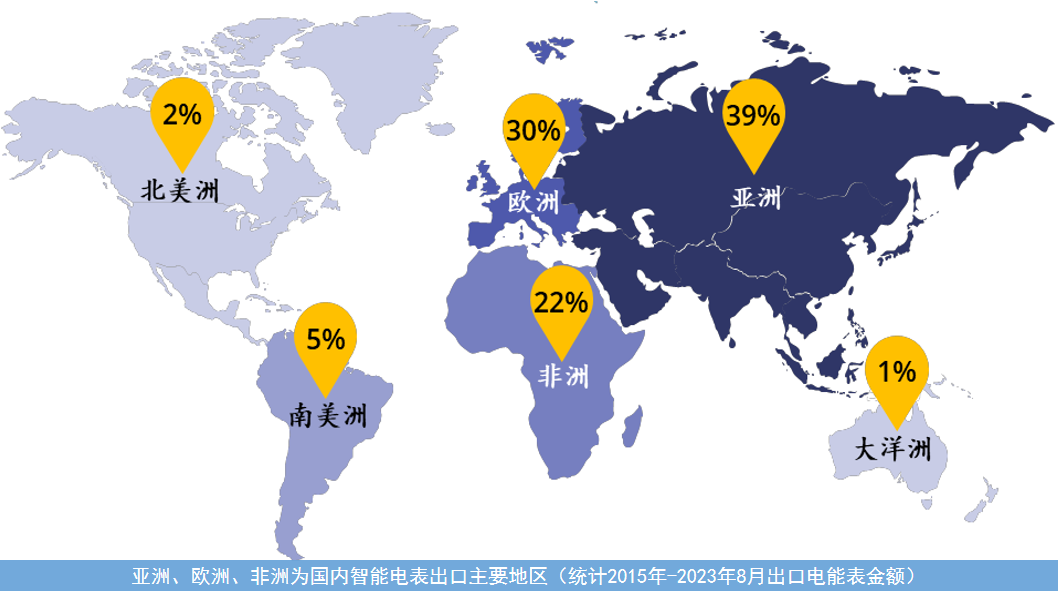
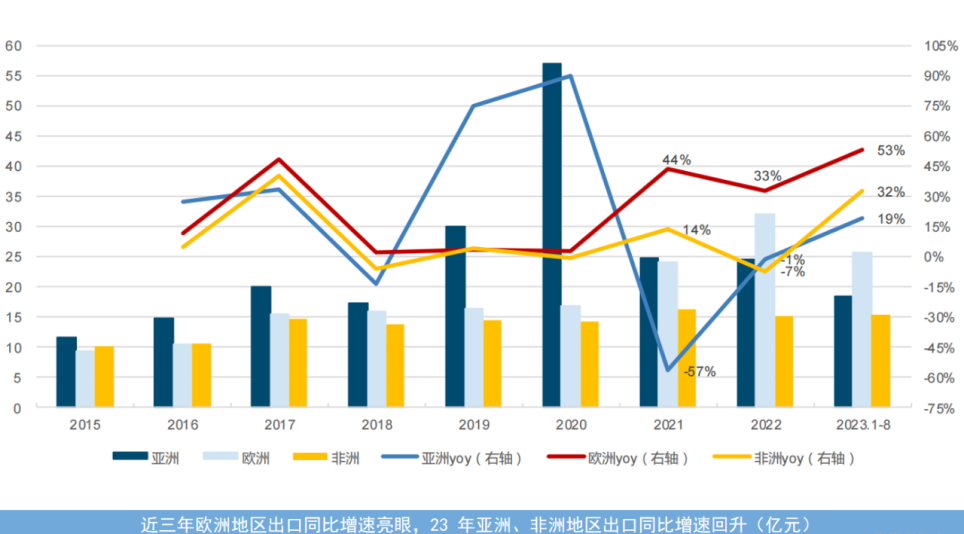
There is a global need for smart meters, an essential end-product, despite varying functional parameters and standards. The underlying logic of these devices can be standardized through platformization and modularization. According to Chinese customs data, exports of smart meters from Chinese manufacturers are primarily concentrated in Asia (39%), Europe (30%), and Africa (22%), with these three markets accounting for over 90% of the total share. North America is challenging to enter due to regulatory reasons, while South America has relatively smaller demand due to financial constraints.
In developed countries, the demand for smart meters primarily comes from the need for periodic upgrades, with replacements required every 7-10 years, creating a stable purchasing cycle. In developing countries, the demand is mainly driven by new installations. This is particularly significant in Africa, where the access to electricity rate is only around 30-40%, indicating a vast market potential.
In terms of growth, the global smart meter market saw an unusual peak in 2020 due to special procurement by Saudi Arabia, but the overall trend remains stable. The European market is growing at a rate of 40-50%, benefiting from a €500 billion grid modernization plan. The African market has a growth rate of 32%, while Asia (excluding China) sees a 19% growth rate. The European market is particularly promising, with substantial investments expected in grid modernization over the next decade.
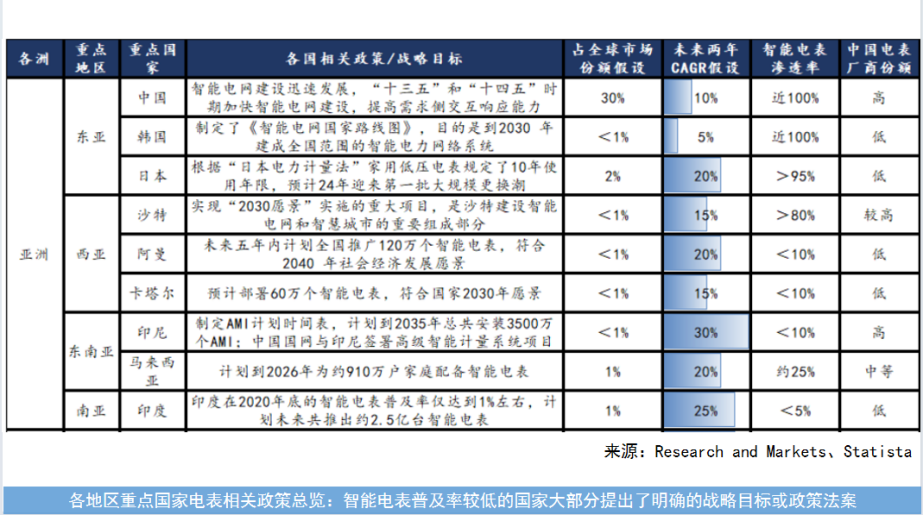
The global smart meter market is significantly influenced by various national policies. Currently, China enjoys a favorable dual market condition, both domestically and internationally, with the domestic market undergoing a new round of grid renovation. In South Korea and Japan, the market share of Chinese companies remains low. However, Saudi Arabia, driven by its Vision 2030 plan, is expected to launch numerous projects, and oil-rich countries like Oman and Qatar also have large-scale stimulus plans.
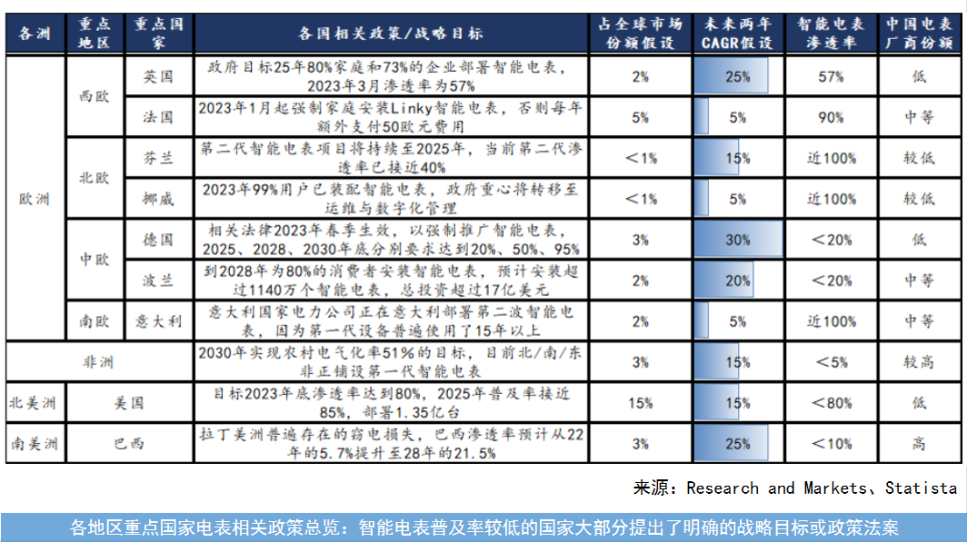
In Southeast Asia, Chinese manufacturers have successfully entered the Indonesian and Malaysian markets, while the Indian market remains closed to Chinese enterprises. Similarly, the US market is also inaccessible to Chinese companies. The European market, however, presents significant demand, with industrial powerhouses like Germany still having relatively low smart meter penetration rates. Chinese companies looking to enter Europe face challenges with their own brand entry but can penetrate the market through ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) arrangements.
The African market is experiencing rapid growth but is highly competitive. The Brazilian market also holds great potential, and Chinese companies are actively entering it. These policy factors provide substantial opportunities for Chinese meter companies.
Belt and Road Initiative in Practice: Rooting in Africa and Expanding Globally
INHE began its international journey on the vast African continent. When the company was founded in 2010, it had neither the funds nor the experience in selling meters, but it was determined to enter the African market. Initially, without a factory, the company could only secure small orders, as large power companies had stringent requirements for suppliers.
To overcome this, the founders decided to purchase land in their hometown to build a factory. They simultaneously negotiated orders while constructing the factory. Despite the factory not being completed, the clients were impressed by the company's sincerity and rapid construction progress. Ultimately, the clients agreed to cooperate, enabling INHE to achieve the remarkable feat of building and launching the factory within the same year.

Mr. Zhu Jianping mentioned, "Choosing the African market at that time was out of necessity, as domestic and Western markets had strict requirements for newly established companies. The African meter market had not yet been the attention of Chinese meter companies, and we were among the first to enter. We chose Sudan, which had been overlooked, partly due to coincidental factors."
In 2011, Sudanese President Bashir visited China, seeking to attract Chinese investment. INHE seized the opportunity and partnered with the Sudanese National Electricity Corporation to provide metering technology and establish assembly lines. This collaboration successfully helped the company accumulate initial capital.

Subsequently, INHE expanded into markets such as Tanzania, South Africa, and Morocco, emerging as a major supplier to the South African National Electricity Company and the Moroccan market in North Africa. The media extensively covered its success in Kenya, labeling it as a benchmark enterprise in Belt and Road electricity projects. Additionally, it became a core supplier in West Africa, particularly in Côte d'Ivoire. Operating in over 30 African countries, the company has grown to become the largest power supplier in the region.
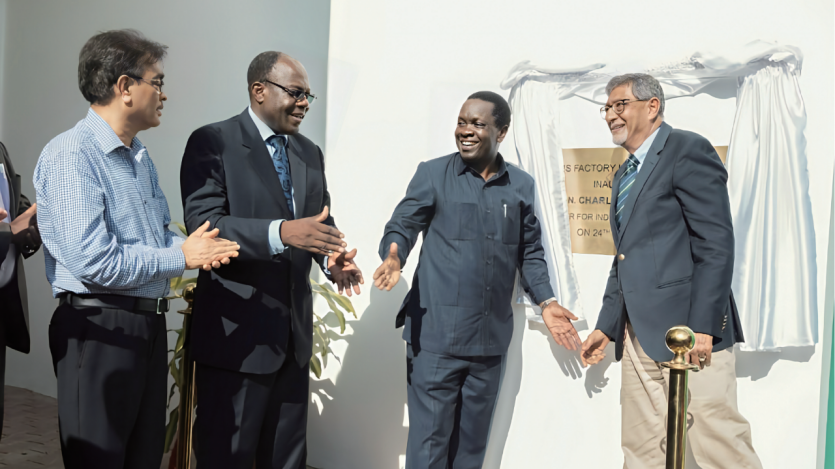
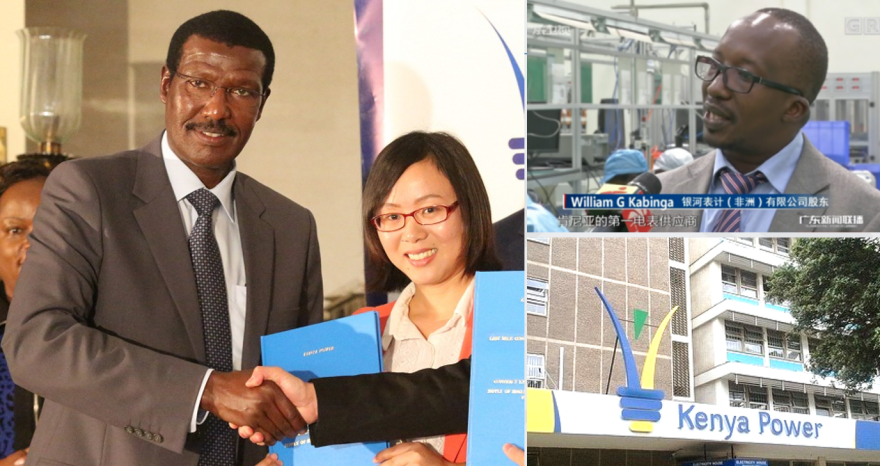


In addition, INHE has achieved significant milestones in the Middle East, Asia, and South America. In the Middle East, it has provided smart meters and system solutions to Palestine and Gaza. In Asia, the company has become a supplier to multiple power companies in Malaysia and Bangladesh. In South America, it has tailored power software systems and smart meter products for the markets in Colombia and Argentina. The company's products have also entered the Eastern European markets gradually, securing significant market share locally through ODM arrangements.



Besides deepening and expanding in overseas markets, INHE has always harbored the hope to "return home". Ultimately, INHE lived up to expectations by becoming a supplier of smart meters to State Grid Corporation of China, achieving stable and consecutive bidding wins with an annual average bid amount exceeding 100 million RMB. This success marks its realization of the dream "coming home"!
The story of INHE is not just a successful case of an enterprise going global but also exemplifies Chinese companies' strategic vision and courage under the Belt and Road Initiative, forging a new chapter of mutual benefit and development. Currently, the company is actively expanding its global market and welcomes aspiring individuals to join us as international salespersons, researchers, or overseas channel partners. Scan the QR code for more information and get in touch.